Weasel ‘discovery’ in Nunavik highlights gap between local knowledge and research
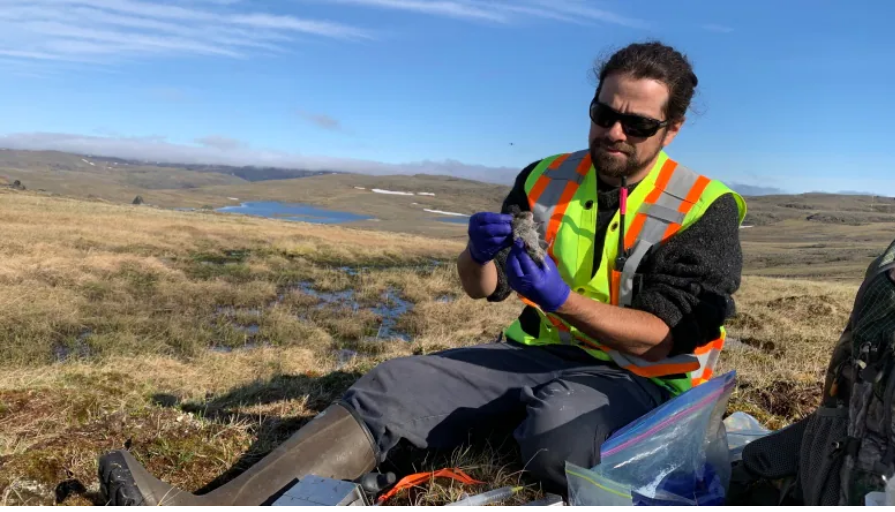

Residents of Salluit, Que., regularly see weasels.
But you wouldn’t know it from the science journals.
A researcher has, for the first time, officially recorded a species of weasel in the region, but says the lack of data on the animal is more surprising than the finding itself.
Least weasels, the smallest member of the weasel family, live across a range of habitats. They’ve been seen as far north as Herschel Island in the western Arctic, at the northern tip of Baffin Island, and in landscapes across the country.
But after discovering a least weasel in their trap in Salluit, researchers Dominique Fauteux and Gregory Rand came to learn the animal had never been mapped in Nunavik.
Fauteux said the discovery exemplifies a disconnect between western research and local knowledge.
“Well, the people there, they already knew it was there. So clearly the lack of communication made these maps incorrect,” he said.
He said creating records of wildlife data in the North is critical to keep track of changes as the climate warms.
“The call is really to gather data for baselines so that we can compare the future of those areas with what’s happening today.”
Fascinating and worrisome
Michael Cameron has lived in Salluit for nearly 40 years. He said the community does see weasels, but that there is only one Inuktitut word for weasel — tigiaq — and that Inuktitut speakers don’t differentiate between types of species.
For that reason, he said, it’s not clear if the least weasel has been in Nunavik all along.
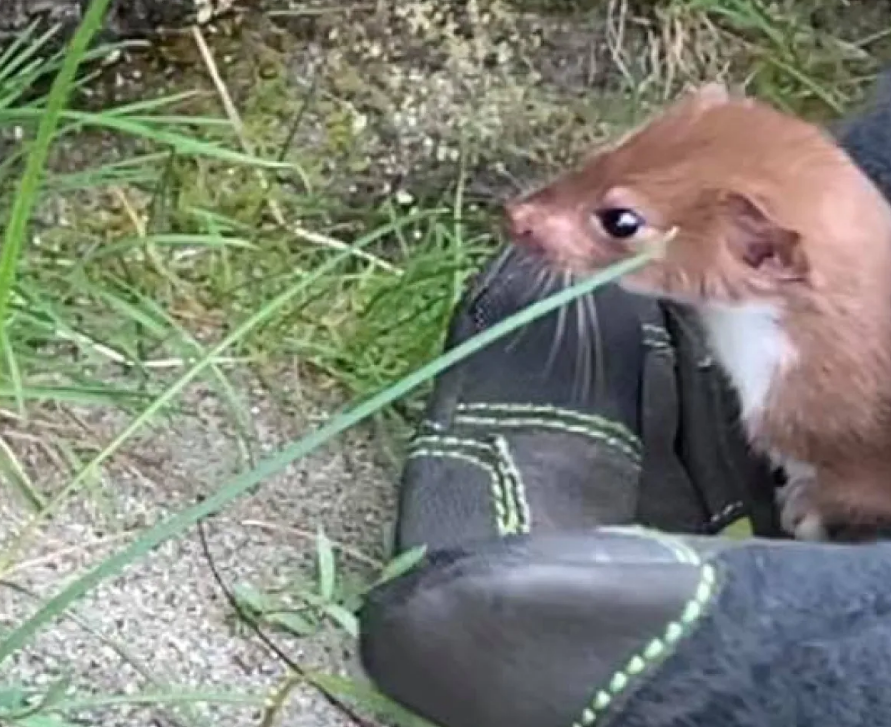

Cameron said tracking that information is becoming increasingly important as more animals migrate north.
“In one sense it’s fascinating, and [in] the other sense it’s worrisome if they come in as invasive species,” he said. He pointed to black bears as an example of an animal that isn’t native to the North, but which is being seen more and more around Salluit.
“To identify the different species is good,” he said, “so that they’re recorded and we get to see what we truly have in the region.”
Paulusie Padlayat, 18, is a hunter who has lived in Salluit all his life. He said he regularly sees weasels out on the land.
It’s not a new observation, either — Padlayat said he’s been seeing them since he joined his father hunting as a kid.
‘It happens every year’
For N.W.T. biodiversity biologist Suzanne Carriere, the “discovery” already known to locals is unsurprising.
“It happens to me every year,” she said. “Somebody saying, ‘We found this and it’s never been discovered before,’ but it was always there. It was just there for people to see it.”
She said biodiversity monitoring programs are not tailored for the North, but that lack of infrastructure, in part, contributes to a rich biodiverse landscape.
It’s “highly important”, she said, that we record the information.
“How are we tracking new species if we don’t know what was there before and what is actually new?”
Carriere said the advent of the internet and technology has helped progress non-invasive monitoring like cameras, new types of sampling and online databases.
Increased communication through social media and through dialogue with locals is part of that too.
Data-deficient, but ‘full of knowledge’
Cameron, from Salluit, is a warden co-ordinator with the Kativik Regional Government but on top of his day job, he volunteers with researchers coming into the community. Cameron helps to co-ordinate logistics and has recently begun connecting researchers with community members.
In Fauteux’s case, he collaborated with the high school and elementary school to share information on his research and hear about the students’ observations.
Fauteux said he plans to maintain that dialogue as he continues monitoring the weasels in the coming years.
“So many areas are data-deficient, but they’re full of knowledge. So we’ve got to work with this and [form] the collaboration between the scientists and the communities in the north.”
Related stories from around the North:
Canada: Climate change driving narwhals to change migration timings
Greenland: Glowing snailfish full of antifreeze proteins found off coast of Greenland, Eye on the Arctic
United States: Alaska’s Bering snow crab, king crab seasons cancelled, The Associated Press



