COVID-19 patients who have infected and inflamed gums run a much higher risk of death and severe complications than those with healthy gums, according to a new international study led by Canadian researchers at McGill University.
The study published in in the Journal of Clinical Periodontology found that COVID-19 patients with gum disease were 3.5 times more likely to be admitted to the intensive care unit, 4.5 times more likely to need a ventilator, and 8.8 times more likely to die when comparing to those without gum disease.
“Looking at the conclusions of our study we can highlight the importance of good oral health in the prevention and management of COVID-19 complications,” said in a statement Belinda Nicolau, contributing author and Full Professor in the Faculty of Dentistry at McGill University. “There is a very strong correlation between periodontitis and disease outcome.”
Periodontitis, also known as gum disease, is a serious infection of the gums that damages supporting tissues of the teeth and if left unmanaged, can lead to bone loss.
‘An invisible pandemic’
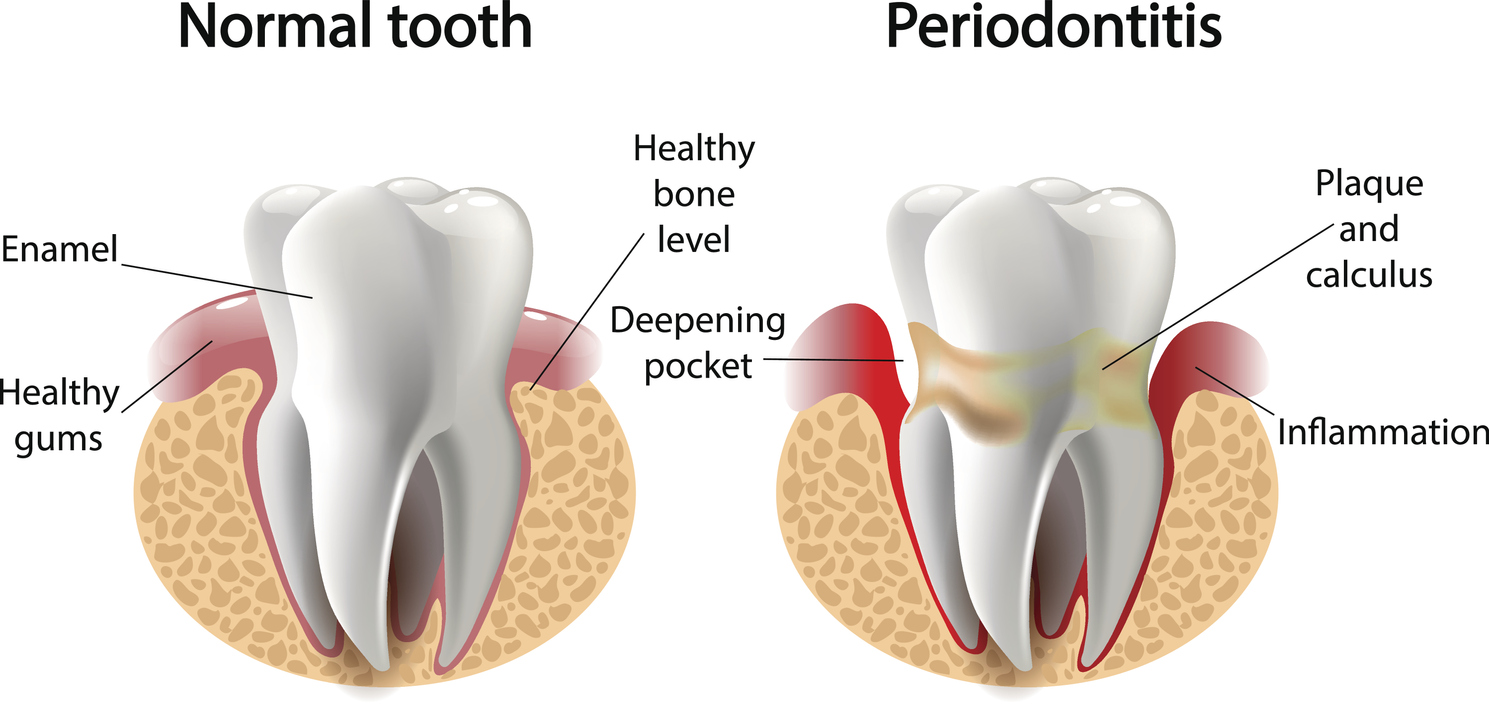
Gum disease begins with plaque. Plaque is clear and sticky and contains germs (or bacteria). It forms on your teeth every day. It also forms where your teeth and your gums meet. If plaque is not removed every day by brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar (also called calculus). (iStock)
According to the Canadian Dental Association, gum disease is one of the most common dental problems in Canadians, with seven out of ten affected to some degree in their lives. Gum disease often develops slowly and without causing any pain. However, it is largely preventable by maintaining good oral hygiene through daily brushing and flossing and getting regular dental check-ups.
Periodontitis has been considered as a risk factor for a number of both oral and systemic diseases, said Wenji Cai, co-author and PhD student from the Faculty of Dentistry.
In fact, periodontitis has been independently associated with several non-communicable diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and even premature mortality.
“It’s an invisible pandemic,” Cai said. “We need to raise awareness of the disease and make more effort to maintain periodontal health, especially during this global pandemic.”
The study by researchers from McGill University, Complutense University of Madrid, and Hamas Medical Corporation of Qatar and Qatar University examined health and dental records of 568 Qatari patients with COVID-19.
It found that blood levels of biomarkers which indicate inflammation in the body were significantly higher in COVID-19 patients with gum disease.
Researchers believe this may explain the higher rates of complications for those patients.
“Periodontitis causes inflammation of the gums and, if left untreated, that inflammation can spread throughout the body,” said Cai.
“In patients with severe cases of COVID-19, the virus causes an inflammatory response that can lead to complications such as being intubated or even death. Our research shows that periodontitis can exasperate this.”






For reasons beyond our control, and for an undetermined period of time, our comment section is now closed. However, our social networks remain open to your contributions.